

Category: Doing Busines in the US
Sep 26, 2022
Coming to America Part 2 - Did I Kill My Business?
Introduction
There are two typical approaches to bringing your company to the United States, set up a new business or buy an existing business. There are benefits and negatives to both, but this article focuses on the option of buying an existing business.
After an extensive search, you find a company that is complementary to your existing business or one that provides a platform to introduce your products and services to the United States market. It has been profitable for several years with high margins and excellent cash flows. All factors are desirable in reducing the risk of your new adventures in North America.
Why might this obvious acquisition be a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase of the organization destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
Skip to the end to find the answer if the details do not interest you.
In Part One of this topic, I briefly discussed the strategy of expanding a European-based business by establishing a presence in the US. I also discussed the importance of NAICS codes in a strategy that includes growing US Federal Government contract revenues using small business set-aside contracts.
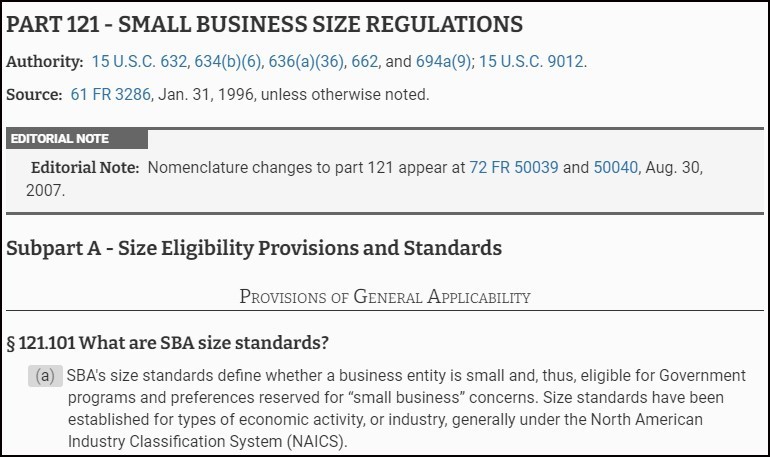
Small Business Size Standards
In the previous article, I described the use of NAICS codes and industry size standards. I the example, 541511 is the code for Custom Computer Programming Services, that have a revenue of limit of $30 million. For clarity, the SBA uses the term annual receipts defined as all revenue plus cost of goods sold.
How are the receipts calculated for your business? Annual receipts for the purpose of small business determination are the average of all receipts over the prior five completed fiscal years. The number of employees includes all individuals employed on a full-time, part-time, or another basis.
All straightforward so far but what adds complexity is that the receipts used in this calculation are those of the company you just bought plus those of any affiliate companies.
What is an Affiliate?
There are many types of potential affiliation, and they are all described in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFRs) 13 CFR part 121.103, the key general principles of affiliation are:
Concerns and entities are affiliates of each other when one controls or has the power to control the other, or a third party or parties controls or has the power to control both. It does not matter whether the control is exercised so long as the power to control exists.
The SBA considers factors such as ownership, management, previous relationships with or ties to another concern, and contractual relationships, in determining whether affiliation exists.
Control may be affirmative or negative. Negative control includes, but is not limited to, instances where a minority shareholder has the ability, under the concern's charter, by-laws, or shareholder's agreement, to prevent a quorum or otherwise block action by the board of directors or shareholders.
Affiliation may be found where an individual, concern, or entity exercises control indirectly through a third party.
In determining the concern's size, SBA counts the receipts, employees, or another measure of the size of the concern whose size is at issue and all of its domestic and foreign affiliates, regardless of whether the affiliates are organized for profit.
Affiliation can be:
Based on stock ownership
Arising under stock options, convertible securities, and agreements to merge
Based on common management
Based on identity of interest
Based on the newly organized concern rule
Receipts or employees attributed to joint venture partners
Additional details can be found in the CFR.
Fortunately, private equity and venture capital ownership of portfolio companies are not considered affiliated entities. The investment company exclusion would cover them.
Why Might Buying a Profitable Business be Damaging to the Strategy?
Previously I asked what factors might make this acquisition a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
If you buy a US business that generates material revenues from small business set-aside contracts, the revenues from your existing interest are now considered affiliate revenues. You may have exceeded the size, and employee limitations for those contracts resulting in the exclusion from any set-aside contract renewals or new Federal contract opportunities applicable to the companies declared NAICS codes. That company with attractive revenues and gross margins may quickly face the challenge of recovering from the loss of existing program government revenues.
Combining affiliate receipts may not result in exceeding the limitations but your strategy is growth. If you are successful, those limits will eventually be exceeded. Consider the impact on the longer-term business strategy and financial modeling when all being well you outgrow the size classifications for your NAICS codes.
Disclaimer
I am not a contract lawyer, and the information in this article should not be considered legal advice. The information should be used as a background primer only.
Introduction
There are two typical approaches to bringing your company to the United States, set up a new business or buy an existing business. There are benefits and negatives to both, but this article focuses on the option of buying an existing business.
After an extensive search, you find a company that is complementary to your existing business or one that provides a platform to introduce your products and services to the United States market. It has been profitable for several years with high margins and excellent cash flows. All factors are desirable in reducing the risk of your new adventures in North America.
Why might this obvious acquisition be a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase of the organization destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
Skip to the end to find the answer if the details do not interest you.
In Part One of this topic, I briefly discussed the strategy of expanding a European-based business by establishing a presence in the US. I also discussed the importance of NAICS codes in a strategy that includes growing US Federal Government contract revenues using small business set-aside contracts.
Small Business Size Standards
In the previous article, I described the use of NAICS codes and industry size standards. I the example, 541511 is the code for Custom Computer Programming Services, that have a revenue of limit of $30 million. For clarity, the SBA uses the term annual receipts defined as all revenue plus cost of goods sold.
How are the receipts calculated for your business? Annual receipts for the purpose of small business determination are the average of all receipts over the prior five completed fiscal years. The number of employees includes all individuals employed on a full-time, part-time, or another basis.
All straightforward so far but what adds complexity is that the receipts used in this calculation are those of the company you just bought plus those of any affiliate companies.
What is an Affiliate?
There are many types of potential affiliation, and they are all described in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFRs) 13 CFR part 121.103, the key general principles of affiliation are:
Concerns and entities are affiliates of each other when one controls or has the power to control the other, or a third party or parties controls or has the power to control both. It does not matter whether the control is exercised so long as the power to control exists.
The SBA considers factors such as ownership, management, previous relationships with or ties to another concern, and contractual relationships, in determining whether affiliation exists.
Control may be affirmative or negative. Negative control includes, but is not limited to, instances where a minority shareholder has the ability, under the concern's charter, by-laws, or shareholder's agreement, to prevent a quorum or otherwise block action by the board of directors or shareholders.
Affiliation may be found where an individual, concern, or entity exercises control indirectly through a third party.
In determining the concern's size, SBA counts the receipts, employees, or another measure of the size of the concern whose size is at issue and all of its domestic and foreign affiliates, regardless of whether the affiliates are organized for profit.
Affiliation can be:
Based on stock ownership
Arising under stock options, convertible securities, and agreements to merge
Based on common management
Based on identity of interest
Based on the newly organized concern rule
Receipts or employees attributed to joint venture partners
Additional details can be found in the CFR.
Fortunately, private equity and venture capital ownership of portfolio companies are not considered affiliated entities. The investment company exclusion would cover them.
Why Might Buying a Profitable Business be Damaging to the Strategy?
Previously I asked what factors might make this acquisition a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
If you buy a US business that generates material revenues from small business set-aside contracts, the revenues from your existing interest are now considered affiliate revenues. You may have exceeded the size, and employee limitations for those contracts resulting in the exclusion from any set-aside contract renewals or new Federal contract opportunities applicable to the companies declared NAICS codes. That company with attractive revenues and gross margins may quickly face the challenge of recovering from the loss of existing program government revenues.
Combining affiliate receipts may not result in exceeding the limitations but your strategy is growth. If you are successful, those limits will eventually be exceeded. Consider the impact on the longer-term business strategy and financial modeling when all being well you outgrow the size classifications for your NAICS codes.
Disclaimer
I am not a contract lawyer, and the information in this article should not be considered legal advice. The information should be used as a background primer only.
Introduction
There are two typical approaches to bringing your company to the United States, set up a new business or buy an existing business. There are benefits and negatives to both, but this article focuses on the option of buying an existing business.
After an extensive search, you find a company that is complementary to your existing business or one that provides a platform to introduce your products and services to the United States market. It has been profitable for several years with high margins and excellent cash flows. All factors are desirable in reducing the risk of your new adventures in North America.
Why might this obvious acquisition be a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase of the organization destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
Skip to the end to find the answer if the details do not interest you.
In Part One of this topic, I briefly discussed the strategy of expanding a European-based business by establishing a presence in the US. I also discussed the importance of NAICS codes in a strategy that includes growing US Federal Government contract revenues using small business set-aside contracts.
Small Business Size Standards
In the previous article, I described the use of NAICS codes and industry size standards. I the example, 541511 is the code for Custom Computer Programming Services, that have a revenue of limit of $30 million. For clarity, the SBA uses the term annual receipts defined as all revenue plus cost of goods sold.
How are the receipts calculated for your business? Annual receipts for the purpose of small business determination are the average of all receipts over the prior five completed fiscal years. The number of employees includes all individuals employed on a full-time, part-time, or another basis.
All straightforward so far but what adds complexity is that the receipts used in this calculation are those of the company you just bought plus those of any affiliate companies.
What is an Affiliate?
There are many types of potential affiliation, and they are all described in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFRs) 13 CFR part 121.103, the key general principles of affiliation are:
Concerns and entities are affiliates of each other when one controls or has the power to control the other, or a third party or parties controls or has the power to control both. It does not matter whether the control is exercised so long as the power to control exists.
The SBA considers factors such as ownership, management, previous relationships with or ties to another concern, and contractual relationships, in determining whether affiliation exists.
Control may be affirmative or negative. Negative control includes, but is not limited to, instances where a minority shareholder has the ability, under the concern's charter, by-laws, or shareholder's agreement, to prevent a quorum or otherwise block action by the board of directors or shareholders.
Affiliation may be found where an individual, concern, or entity exercises control indirectly through a third party.
In determining the concern's size, SBA counts the receipts, employees, or another measure of the size of the concern whose size is at issue and all of its domestic and foreign affiliates, regardless of whether the affiliates are organized for profit.
Affiliation can be:
Based on stock ownership
Arising under stock options, convertible securities, and agreements to merge
Based on common management
Based on identity of interest
Based on the newly organized concern rule
Receipts or employees attributed to joint venture partners
Additional details can be found in the CFR.
Fortunately, private equity and venture capital ownership of portfolio companies are not considered affiliated entities. The investment company exclusion would cover them.
Why Might Buying a Profitable Business be Damaging to the Strategy?
Previously I asked what factors might make this acquisition a poor decision, and furthermore, how may your purchase destroy the financial performance of your new subsidiary?
If you buy a US business that generates material revenues from small business set-aside contracts, the revenues from your existing interest are now considered affiliate revenues. You may have exceeded the size, and employee limitations for those contracts resulting in the exclusion from any set-aside contract renewals or new Federal contract opportunities applicable to the companies declared NAICS codes. That company with attractive revenues and gross margins may quickly face the challenge of recovering from the loss of existing program government revenues.
Combining affiliate receipts may not result in exceeding the limitations but your strategy is growth. If you are successful, those limits will eventually be exceeded. Consider the impact on the longer-term business strategy and financial modeling when all being well you outgrow the size classifications for your NAICS codes.
Disclaimer
I am not a contract lawyer, and the information in this article should not be considered legal advice. The information should be used as a background primer only.

Jan 31, 2025
The Hidden Crisis in Business: When Optimization Masks a Lack of True Differentiation
When revenue stalls, leaders rush to optimize processes, trim costs, and demand more from teams. But what if the problem isn’t how well you’re executing—it’s that no one cares what you’re executing?

Jan 11, 2025
Strategy vs. Execution: Why Execution Must Come First
There’s a popular saying in business: “Vision without execution is just hallucination.” While a bit tongue-in-cheek, it captures an important lesson. Regardless of how impressive or innovative your strategy might be, if your organization can’t implement it effectively, the strategy itself is doomed.

Jan 10, 2025
From the Control Tower to the Corner Office: A Lesson in Leadership and Communication
As an air traffic controller, proactive thinking is survival. You predict weather changes, anticipate pilot error, and arrange flight paths with near-clairvoyant foresight. In corporate leadership, being proactive is equally critical. But in business, you have an entire workforce that needs to understand why you’re making the calls that you do.

Jan 31, 2025
The Hidden Crisis in Business: When Optimization Masks a Lack of True Differentiation
When revenue stalls, leaders rush to optimize processes, trim costs, and demand more from teams. But what if the problem isn’t how well you’re executing—it’s that no one cares what you’re executing?

Jan 11, 2025
Strategy vs. Execution: Why Execution Must Come First
There’s a popular saying in business: “Vision without execution is just hallucination.” While a bit tongue-in-cheek, it captures an important lesson. Regardless of how impressive or innovative your strategy might be, if your organization can’t implement it effectively, the strategy itself is doomed.

Jan 31, 2025
The Hidden Crisis in Business: When Optimization Masks a Lack of True Differentiation
When revenue stalls, leaders rush to optimize processes, trim costs, and demand more from teams. But what if the problem isn’t how well you’re executing—it’s that no one cares what you’re executing?
NeWTHISTle Consulting
DELIVERING CLARITY FROM COMPLEXITY
Copyright © 2024 NewThistle Consulting LLC. All Rights Reserved
NeWTHISTle Consulting
DELIVERING CLARITY FROM COMPLEXITY
Copyright © 2024 NewThistle Consulting LLC. All Rights Reserved
NeWTHISTle Consulting
DELIVERING CLARITY FROM COMPLEXITY
Copyright © 2024 NewThistle Consulting LLC. All Rights Reserved
